Understanding VRF Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding VRF Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s world, energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability are driving the innovations in HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems. One such breakthrough in this field is the Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) system. VRF technology has gained tremendous popularity due to its flexibility, energy efficiency, and ability to provide precise control of indoor climates. This blog post will explore what VRF systems are, how they work, their benefits, and their applications.
What is a VRF System?
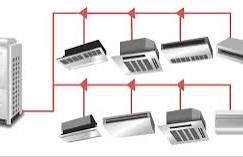
A VRF system is a type of HVAC technology that uses refrigerants to heat or cool a building. It works by adjusting the flow of refrigerant to indoor units based on the specific heating and cooling requirements of individual zones within a building. VRF systems are designed to provide flexible, energy-efficient heating and cooling for both residential and commercial applications.
The key characteristic of a VRF system is its ability to control the amount of refrigerant flowing to each indoor unit based on demand. This allows for the simultaneous heating and cooling of different areas of a building, making it ideal for spaces with varying temperature needs.
How Does a VRF System Work?
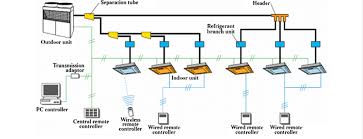
At the heart of a VRF system is the outdoor unit, which is connected to multiple indoor units through refrigerant piping. The system uses an inverter-driven compressor to regulate the flow of refrigerant, making it more efficient than traditional HVAC systems. Let’s break down how it works:
- Outdoor Unit (Compressor): The outdoor unit houses a compressor that regulates the flow of refrigerant. In a VRF system, the compressor is variable-speed, meaning it adjusts the speed of operation based on the demand for heating or cooling. This is in contrast to traditional systems that operate at a fixed speed, making VRF systems more energy-efficient.
- Refrigerant Piping: The outdoor unit is connected to multiple indoor units via a network of refrigerant piping. The refrigerant moves through these pipes, transferring heat or cold to the indoor units.
- Indoor Units (Air Handling Units): Indoor units are installed in different rooms or zones within a building. Each unit can independently control the temperature of its designated area, which means occupants can adjust the comfort levels in their space without affecting other areas. These units come in various forms, such as wall-mounted, ceiling-suspended, or concealed units, depending on the design and space requirements.
- Inverter Technology: The inverter-driven compressor adjusts its speed depending on the heating or cooling demand, allowing the system to operate at an optimal capacity. This is much more energy-efficient than conventional systems that constantly switch on and off, consuming more energy.
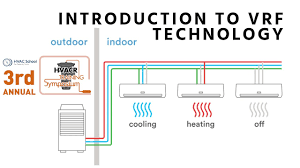
- Heat Recovery and Heat Pump Systems: There are two types of VRF systems: heat pump systems and heat recovery systems. A heat pump system provides either cooling or heating depending on the time of year. A heat recovery system, on the other hand, can provide both cooling and heating simultaneously. For example, one part of the building could be cooled while another part is being heated.

Types of VRF Systems
There are two primary types of VRF systems: heat pump systems and heat recovery systems.
1. Heat Pump VRF System
In a heat pump VRF system, the outdoor unit is responsible for either cooling or heating, but not both at the same time. The system is ideal for buildings where simultaneous heating and cooling are not required. In the summer, the system will cool all zones, while in the winter, it will provide heating for all indoor units.
2. Heat Recovery VRF System
A heat recovery VRF system, on the other hand, can provide both heating and cooling simultaneously. This is particularly useful in larger buildings, such as commercial or multi-purpose spaces, where different zones might need different temperatures. For instance, one area of the building may require cooling while another area needs heating. The system is designed to transfer excess heat from one zone to another, increasing energy efficiency.
Key Benefits of VRF Systems
There are several reasons why VRF systems have become a preferred choice for both residential and commercial HVAC needs. Let’s take a look at the key benefits of using a VRF system:
1. Energy Efficiency
The inverter technology used in VRF systems allows for more precise control of the compressor’s speed, enabling the system to operate at varying capacities based on real-time demand. This reduces the energy consumption significantly compared to traditional HVAC systems that operate at full capacity all the time. Additionally, heat recovery systems can transfer excess heat from one area to another, further improving energy efficiency.
2. Zoning and Flexibility
One of the most significant advantages of a VRF system is its zoning capability. The system allows for the independent control of temperature in different areas of a building. For example, in a multi-story building, different floors can be cooled or heated according to individual preferences. This zoning flexibility ensures that energy is used efficiently, as unoccupied or unused areas can be set to a lower temperature.
3. Compact and Flexible Installation
VRF systems are more compact than traditional HVAC systems, making them ideal for buildings with limited space. The indoor units can be installed in a variety of configurations, including ceiling-mounted, floor-standing, or wall-mounted units, offering flexibility for both new constructions and retrofits. Additionally, the refrigerant piping is relatively small and can be routed to multiple indoor units, which reduces the need for large ductwork.
4. Comfort and Control
VRF systems provide superior comfort by offering precise temperature control. The ability to adjust the settings in individual rooms or zones means that people can enjoy personalized comfort without affecting others. The systems operate quietly, ensuring minimal disruption to occupants.
5. Low Maintenance Costs
Due to the lack of ducts and the advanced technology, VRF systems generally require less maintenance than traditional HVAC systems. The components of a VRF system are also more durable, which leads to lower repair and replacement costs in the long run.
6. Sustainability
Since VRF systems are energy-efficient and capable of utilizing renewable energy sources, they have a smaller environmental footprint compared to conventional systems. Many VRF systems are compatible with eco-friendly refrigerants, contributing to sustainability goals.
Applications of VRF Systems
VRF systems are versatile and can be applied in a wide range of building types, including residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Here are a few common applications:
1. Residential Buildings
In residential buildings, VRF systems can be used to provide heating and cooling to individual rooms or zones. This is especially beneficial in large homes or multi-family units where different rooms have different temperature requirements. The system ensures optimal comfort while keeping energy costs down.
2. Commercial Buildings
Commercial spaces such as offices, retail stores, hotels, and restaurants can greatly benefit from VRF systems. The ability to control the temperature in different areas allows for efficient climate management in spaces with diverse needs. For example, in a hotel, one part of the building may require heating while another needs cooling, and a VRF system can meet these demands simultaneously.
3. Educational Institutions
Schools, universities, and other educational institutions often have large, diverse buildings with varying temperature needs. VRF systems can provide heating and cooling to individual classrooms, offices, and common areas, ensuring that each room has the optimal temperature for learning and comfort.
4. Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities require precise temperature control to ensure patient comfort and safety. VRF systems can be used in these environments to maintain appropriate temperatures in patient rooms, operating theaters, and common areas.
5. Industrial Facilities
Industrial facilities that require climate control for both personnel comfort and equipment functioning can benefit from VRF systems. These systems offer energy-efficient cooling and heating solutions for manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and data centers.
Challenges and Considerations
While VRF systems offer numerous benefits, there are some considerations to keep in mind when deciding to implement one.
- High Initial Cost: The initial investment for a VRF system can be higher than that of traditional HVAC systems, primarily due to the advanced technology and installation requirements. However, the energy savings over time can offset these costs.
- Complex Installation: Installing a VRF system requires a skilled technician, and the refrigerant piping needs to be precisely installed. It is important to hire experienced professionals to ensure that the system operates efficiently.
- Space Requirements: While VRF systems are more compact than traditional systems, they still require space for the outdoor unit and refrigerant piping. In certain applications, the space needed for these components may be a limiting factor.
- Maintenance: While VRF systems generally require less maintenance than traditional HVAC systems, regular servicing is still necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Conclusion
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems represent a significant advancement in HVAC technology. They provide superior energy efficiency, comfort, and flexibility, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications. Their ability to offer precise control over indoor climates while minimizing energy consumption makes them a compelling choice for modern buildings.
Despite the higher initial cost and installation complexity, the long-term benefits of a VRF system—including energy savings, reduced maintenance, and improved comfort—make it a valuable investment for building owners and operators. As energy efficiency and sustainability continue to drive building design and construction, VRF systems are likely to become even more popular and essential in creating comfortable, eco-friendly environments.
